Table of Contents Show
- Signs of Declining Health
- Factors that Contribute to Health Decline
- Age-Related Health Decline
- Genetic Factors in Health Decline
- Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Health Decline
- Effects of Environmental Factors on Health Decline
- Role of Chronic Diseases in Health Decline
- Relationship Between Stress, Mental Health, and Health Decline
- Preventive Measures for Avoiding Health Decline
- Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Are you curious about the factors that contribute to a decline in health? In this article, we will explore the various circumstances that can lead to a deterioration in your overall well-being. From lifestyle choices to age-related changes, understanding when “Health Decline” health may start declining is essential for proactive self-care. So, let’s uncover the signs and causes that can impact your physical and mental well-being.
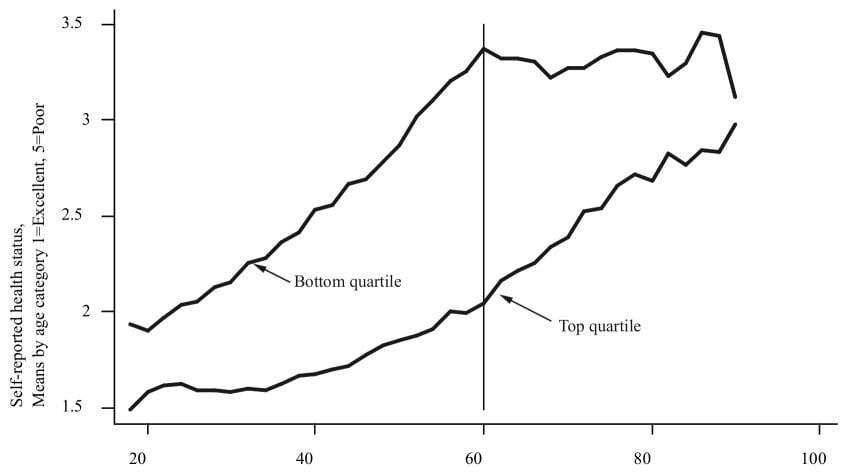
This image is property of www.nber.org.
Signs of Declining Health
As you go through life, it’s important to be aware of the signs that may indicate declining health. These signs can manifest in various ways and serve as early warnings that something might not be right. Being able to recognize these signs is crucial in seeking timely medical attention and taking steps towards improving your well-being. Here are some common signs of declining health:
Weight Loss or Gain
One of the signs that could indicate declining health is a significant and unexplained weight loss or gain. Sudden changes in weight may be a cause for concern as they could be indicative of underlying health issues. It’s important to pay attention to any unexplained weight fluctuations and consult a healthcare professional if you notice such changes.
Fatigue and Lack of Energy
Feeling constantly tired or having a lack of energy can also be signs of declining health. While it’s natural to feel tired from time to time, persistent fatigue can be a symptom of an underlying health condition. If you find yourself constantly feeling exhausted despite getting enough rest, it may be worth discussing your concerns with a healthcare provider.
Frequent Illnesses
Experiencing frequent illnesses, such as colds, infections, or other ailments, can also be an indication that your health is declining. When your immune system is compromised, it becomes easier for illnesses to take hold. If you find yourself falling ill more often than usual, it’s advisable to seek medical advice to identify any potential underlying causes.
Chronic Pain
Chronic pain refers to persistent, long-lasting pain that can negatively impact your quality of life. This type of pain can be caused by various factors, including injuries, inflammation, and underlying health conditions. If you’re experiencing ongoing pain that doesn’t seem to go away, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional who can help diagnose and manage the underlying cause.
Mental Health Changes
Changes in your mental health can also be a sign of declining overall health. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, or mood disorders can have a significant impact on your well-being. If you notice persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest in activities, difficulty concentrating, or changes in mood, it’s essential to reach out to a mental health professional for guidance and support.
Factors that Contribute to Health Decline
While declining health can affect anyone at any stage of life, there are several common factors that can contribute to this decline. These factors vary from individual to individual and understanding them can help in taking proactive steps towards maintaining overall well-being. Here are some factors that can contribute to health decline:
Age
Age is a significant factor in health decline. As you grow older, your body undergoes natural changes that can affect various aspects of your health. In each stage of life, from early adulthood to middle age and old age, different health challenges may arise. Being aware of these age-related changes can help you understand what to expect and take appropriate measures to protect your health.
Genetics
Genetic factors can play a role in health decline. Certain inherited conditions or gene mutations can increase the risk of developing specific health problems. While you can’t change your genetic makeup, understanding your family’s medical history can help you and your healthcare provider identify potential health risks early on and develop strategies to manage them effectively.
Lifestyle Choices
The choices you make in your daily life can have a significant impact on your health. Your diet, level of physical activity, tobacco and alcohol use, and sleep patterns all play a role in determining your overall well-being. Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as following a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and getting enough rest, can promote good health and reduce the risk of health decline.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, both external and internal to your living environment, can influence your health. Air pollution, water contamination, exposure to chemicals, and even noise pollution can have adverse effects on your well-being. Being mindful of your surroundings and taking measures to reduce exposure to harmful substances can help protect your health and prevent future health decline.
Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, cancer, diabetes, respiratory disorders, and neurological disorders, can significantly impact your health and contribute to decline. These conditions often require ongoing management and treatment to reduce symptoms and prevent further health complications. Regular medical check-ups and proactive management of chronic diseases are crucial in maintaining overall health.
Stress and Mental Health
Stress and mental health can also contribute to health decline. Elevated stress levels can take a toll on both your physical and mental well-being, leading to a range of health problems. Additionally, mental health conditions like depression and anxiety can have a profound impact on your overall health. Prioritizing stress management techniques and seeking appropriate mental health support are essential in preventing health decline.
This image is property of www.nber.org.
Age-Related Health Decline
As mentioned earlier, age is a significant contributing factor to health decline. Different stages of life present unique health challenges, and understanding how your health may change during each phase can help you take appropriate measures to maintain your well-being. Let’s explore the age-related health decline in early adulthood, middle age, and old age:
Early Adulthood
In early adulthood, when you’re in your 20s and 30s, you may generally enjoy good health. However, it’s important not to take your health for granted. This is a crucial time to establish healthy lifestyle habits that can have a long-lasting impact on your well-being. It’s essential to maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, get sufficient sleep, manage stress effectively, and avoid unhealthy habits such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption.
Middle Age
As you enter middle age, typically in your 40s and 50s, certain health challenges become more prevalent. Metabolism may slow down, making it easier to gain weight and harder to lose it. Hormonal changes, such as menopause in women, can also affect overall health. Regular screenings for conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers become increasingly important during this stage to catch any potential health problems early on.
Old Age
In old age, typically 60 and above, your body undergoes further changes, and health concerns can become more frequent. Chronic health conditions and age-related diseases may become more prevalent. It’s crucial to prioritize preventive healthcare, including regular check-ups, screenings, and adhering to prescribed medications. Staying socially engaged, maintaining mental and physical activity, and having a strong support system can also contribute to healthy aging.
Genetic Factors in Health Decline
Genetic factors can play a significant role in health decline. Understanding your genetic predisposition to certain conditions can help you and your healthcare provider develop a proactive approach to managing your health effectively. Here are two primary genetic factors that can contribute to health decline:
Inherited Conditions
Certain health conditions have a genetic component and can run in families. These inherited conditions often occur due to gene mutations or variations passed down from one generation to another. Examples include conditions like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and certain types of cancer. Knowing your family medical history and discussing it with your healthcare provider can help determine if you are at an increased risk and enable you to make informed choices about your health.
Gene Mutations
Gene mutations, or changes in the DNA sequence, can also contribute to the development of certain health conditions. Some gene mutations are inherited, while others may occur spontaneously. Mutations can affect various aspects of health, including metabolism, immune function, and susceptibility to certain diseases. Genetic testing and counseling can provide valuable insights into any potential gene mutations you may carry and help guide your healthcare decisions.
This image is property of www.metrophysio.co.uk.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Health Decline
The lifestyle choices you make on a daily basis can have a profound impact on your overall health and significantly contribute to health decline. By adopting healthy habits and making conscious choices, you can promote your well-being and reduce the risk of developing certain health conditions. Here are some key lifestyle choices that can impact your health decline:
Diet and Nutrition
Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet is essential for optimal health. Nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provide the necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to support your body’s functions. Avoiding excessive sugar, processed foods, unhealthy fats, and sodium helps reduce the risk of obesity, heart disease, and other chronic conditions.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining good health. Engaging in moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, for at least 150 minutes per week can help improve cardiovascular health, strengthen muscles and bones, and boost overall well-being. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises can help maintain muscle mass and flexibility as you age.
Tobacco and Alcohol Use
Tobacco use, including smoking cigarettes or using smokeless tobacco products, can have severe detrimental effects on health. Smoking is a major risk factor for various cancers, heart disease, respiratory disorders, and other health conditions. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage, increased risk of certain cancers, and other significant health problems. Quitting tobacco and drinking in moderation or abstaining altogether can greatly reduce the risk of health decline.
Sleep Patterns
Getting enough quality sleep is essential for overall health and well-being. Adequate sleep allows your body to repair and recharge, both physically and mentally. Chronic lack of sleep or poor sleep quality can contribute to an array of health issues, including increased risk of obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and mental health problems. Establishing a regular sleep routine, creating a conducive sleep environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene are all important in ensuring restful sleep.
Effects of Environmental Factors on Health Decline
Environmental factors, both external and internal, can impact your overall health and contribute to health decline. Being aware of potential environmental hazards and taking preventive measures can help protect your well-being. Here are some effects of environmental factors on health decline:
Air Pollution
Exposure to air pollution, whether from outdoor sources or indoor pollutants, can have adverse effects on respiratory health and overall well-being. Fine particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and other pollutants can contribute to the development or worsening of respiratory disorders, cardiovascular disease, and other health problems. Reducing exposure to air pollution by staying indoors during peak pollution times and using air purifiers can help mitigate these risks.
Water Contamination
Water contamination can pose significant risks to health. Exposure to pollutants, such as heavy metals, chemicals, bacteria, and parasites, through contaminated water sources, can lead to gastrointestinal issues, infections, and other health problems. Ensuring access to clean, safe drinking water and using appropriate water filtration methods can help reduce the risks associated with water contamination.
Exposure to Chemicals
Daily exposure to chemicals in household products, personal care items, or industrial settings can also impact health. Certain chemicals, like pesticides, cleaning agents, or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in paints or adhesives, can have harmful effects on respiratory health, neurological function, and hormone regulation. Minimizing exposure to these chemicals by using natural or low-toxicity alternatives, proper ventilation, and protective gear can help protect your health.
Noise Pollution
Excessive or prolonged exposure to loud noises can negatively impact health and well-being. Noise pollution can lead to stress, sleep disturbances, hearing loss, and increased risk of cardiovascular problems. Taking measures to reduce noise exposure, such as using ear protection, soundproofing your living space, or finding quiet environments for relaxation, can help mitigate these risks.
This image is property of thesocietypages.org.
Role of Chronic Diseases in Health Decline
Chronic diseases play a significant role in overall health decline. These conditions are often long-lasting and may require ongoing management and treatment to prevent further health complications. Here are some common chronic diseases and their impact on health decline:
Heart Disease
Heart disease, including conditions like coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias, is a leading cause of health decline worldwide. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, smoking, and high blood pressure or cholesterol levels can contribute to the development of heart disease. Early detection, lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and surgical interventions, when necessary, can help manage heart disease and prevent further health decline.
Cancer
Cancer is a complex disease with various forms and can greatly impact health and well-being. Risk factors for cancer include genetic predisposition, exposure to environmental toxins, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, lack of physical activity, and certain infections. Early detection through screenings, timely treatment interventions, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a vital role in managing cancer and improving long-term outcomes.
Diabetes
Diabetes, both type 1 and type 2, is a metabolic disorder characterized by abnormal blood sugar levels. Unmanaged diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. Lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and medication adherence, are key in managing diabetes and preventing its complications.
Respiratory Disorders
Respiratory disorders, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and pulmonary fibrosis, can significantly impact lung health and overall well-being. Risk factors for these conditions include smoking, exposure to environmental pollutants, and genetic predisposition. Proper diagnosis, medication management, pulmonary rehabilitation, and avoiding triggers can help manage respiratory disorders and alleviate symptoms.
Neurological Disorders
Neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and epilepsy, affect the central nervous system and can have a profound impact on health. These conditions often require ongoing treatment, medication management, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and slow their progression. Early detection, appropriate medical care, and a comprehensive support system are crucial in navigating the complexities of neurological disorders.
Relationship Between Stress, Mental Health, and Health Decline
The relationship between stress, mental health, and health decline is complex and interconnected. Elevated stress levels and untreated mental health conditions can have significant implications for your overall well-being. Understanding this relationship and taking proactive steps to address stress and mental health concerns are essential for maintaining good health. Here’s how stress and mental health can impact health decline:
Elevated Stress Levels
Prolonged or chronic stress can take a toll on your physical and mental health. It can affect key bodily systems, including the cardiovascular, immune, and digestive systems, leading to increased vulnerability to various health problems. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and seeking support from loved ones or mental health professionals can help restore balance and reduce the impact of stress on health.
Depression and Anxiety
Depression and anxiety are common mental health conditions that can significantly impact overall well-being. Both conditions are associated with increased risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Additionally, depression and anxiety can affect sleep patterns, appetite, energy levels, and the ability to engage in healthy behaviors. Seeking appropriate mental health support and treatment is crucial in managing these conditions and preventing further health decline.
Impact on Physical Health
Untreated mental health conditions can have direct physiological effects on the body. They can weaken the immune system, increase inflammation, disrupt hormonal balance, and contribute to conditions such as chronic pain and autoimmune disorders. Moreover, mental health concerns can impair self-care practices, such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in physical activity, and seeking regular medical care. Addressing mental health needs and considering a holistic approach to well-being can have a positive impact on your physical health and overall quality of life.
This image is property of qph.cf2.quoracdn.net.
Preventive Measures for Avoiding Health Decline
Prevention is key when it comes to avoiding health decline. By making proactive choices and prioritizing your well-being, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing health problems. Here are some preventive measures you can take to avoid health decline:
Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are essential for early detection and intervention. Schedule routine visits with your healthcare provider, even if you feel healthy, to monitor your overall health and identify any potential issues at an early stage. These check-ups often include screenings, blood tests, and assessments to evaluate your risk factors and provide preventive guidance.
Healthy Diet and Exercise
Maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise are crucial in promoting good health. Choose nutrient-rich foods, emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, combining cardiovascular activities with strength training to support overall fitness. Consulting a nutritionist and personal trainer can help tailor healthy eating and exercise plans according to your individual needs.
Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for your overall well-being. Establish a regular sleep routine, create a conducive sleep environment, and prioritize restful sleep. Aim for the recommended 7-9 hours of sleep per night and address any potential sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or insomnia, with the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Stress Management Techniques
Implement stress management techniques to reduce the impact of stress on your health. This may include mindfulness practices, relaxation exercises, deep breathing techniques, engaging in hobbies, connecting with loved ones, and seeking professional counseling or therapy when needed. Developing healthy coping mechanisms and setting boundaries can help in managing stress effectively.
Mental Health Support
Recognize the importance of mental health and seek appropriate support when needed. Reach out to mental health professionals for counseling, therapy, or medication management if you’re experiencing persistent feelings of sadness, anxiety, or other mental health concerns. Prioritizing self-care, engaging in activities that bring joy, and cultivating a positive support network are also essential components of maintaining mental well-being.
Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Early detection and intervention can greatly impact your health outcomes and prevent further decline. Recognizing warning signs, seeking medical attention, and creating an individualized plan in collaboration with your healthcare provider are crucial steps in maintaining your health. Here’s why early detection and intervention are important:
Recognizing Warning Signs
Being attuned to your body and recognizing warning signs of potential health problems can help identify issues before they become severe. Educate yourself about the signs and symptoms associated with different health conditions, and don’t ignore any persistent changes or symptoms that concern you. Promptly address any emerging concerns with your healthcare provider to facilitate early diagnosis and treatment.
Seeking Medical Attention
When you notice symptoms or warning signs, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention. Timely medical evaluation can help diagnose underlying conditions and determine appropriate treatment plans. Regular check-ups and screenings can detect potential health problems early on, giving you a better chance of successful outcomes and preventing further decline.
Risk Assessment and Screening
Based on your age, family medical history, lifestyle factors, and other individual factors, your healthcare provider can perform risk assessments and recommend appropriate screenings. These screenings can help identify risk factors or early signs of diseases like cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and more. By understanding and addressing your specific risk factors, you can take proactive steps towards managing or preventing potential health problems.
Creating an Individualized Plan
Collaborating with your healthcare provider to create an individualized plan is essential for maintaining your health. Based on your medical history, lifestyle, and goals, your healthcare provider can develop a customized plan that may include preventive measures, screenings, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate treatments if needed. Regular follow-ups and adherence to your healthcare plan can contribute to long-term health and well-being.
In conclusion, being aware of the signs of declining health is crucial in maintaining your overall well-being. Factors such as age, genetics, lifestyle choices, environmental factors, chronic diseases, and stress can contribute to health decline. Understanding the impact of these factors and taking appropriate preventive measures, such as regular check-ups, healthy diet and exercise, stress management, and mental health support, can help avoid health decline. Early detection and intervention are also vital in improving health outcomes. By recognizing warning signs, seeking medical attention, and creating an individualized plan, you can take control of your health and ensure a healthier future. Remember, making small changes today can have a significant positive impact on your health in the long run.